What is Cell Treatment?
What is cell treatment?
Cell therapy is a new medical field that involves using cells to treat or cure diseases thesportship.
These cell therapies may include hematopoietic stem cell transplants (which treat
blood cancers like leukemia), bone marrow-derived stem cells, mesenchymal stem
cells and other types of specialized cell populations.

The Cell Therapy Program at Dana-Farber Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center
builds on our expertise in stem cell transplantation to deliver effective treatments
for patients with certain cancers, chronic conditions, and regenerative disorders.
This approach to treatment offers fewer side effects, easier recovery and less risk of
immunological complications than traditional organ transplantation.
Stem Cells as a Treatment Option for Parkinson’s Disease
Several studies have shown that grafting fetal tissues into patients with Parkinson’s
disease can improve some symptoms, but it has not been proven safe or effective in
treating the condition. However, a growing number of clinical trials have
demonstrated that certain types of stem cells can restore lost function in certain
brain disorders.
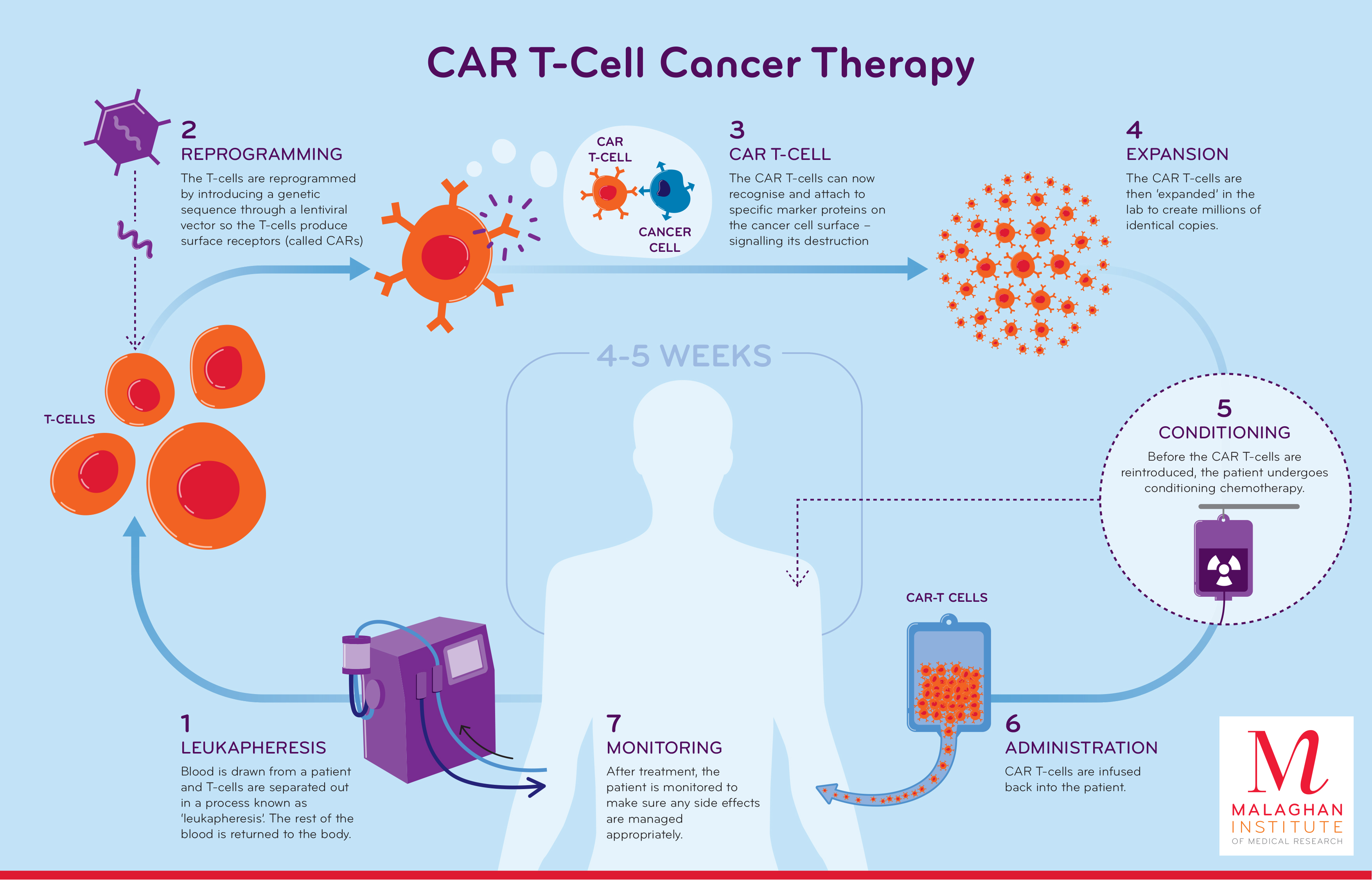
CAR T-Cell Therapies for Leukemia and Lymphoma
Many cancers produce antigens on their surface, which immune cells can detect.
These antigens can help the immune cells attack the cancer cells. In a cell therapy
called chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, the patient’s own T cells are
changed in the lab so that they have a specific gene that helps them attach to
antigens on cancer cells.
This can destroy the cancer cells without killing healthy cells. The resulting immune
cells can also be used to treat other serious conditions, including leukemia and
lymphoma.
Stem Cells as regenerative Treatment for Heart Failure
A number of studies have shown that some adult stem cells can be guided to
become heart-like cells and can repair damaged heart tissue in people. This is
known as regenerative medicine and researchers are working to learn more about it
so that we can use it to treat others.
Some regenerative therapies are FDA-approved, such as hematopoietic stem cell
(blood-forming) transplantation for blood cancers and other disorders. Other cell
therapies are still in clinical trials and could be a treatment option for other
conditions.
Cellular Therapy for Neurodegenerative Disorders
A number of animal models have been studied to evaluate the effects of cellular
therapies for neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple
sclerosis. The results of these tests have been promising, showing that grafting
certain cellular sources to the brain can help patients recover and reduce the need
for dopaminergic medications.
In other regenerative cell therapies, the patient’s own cells are cultivated or
modified outside of the body before being injected into the patient. These cells may
originate from the patient (autologous) or a donor (allogeneic).
In addition to regenerative therapies, researchers are studying how stem cell-
derived cells can be used to treat other types of cancers and other health problems.
These include a variety of types of T cells, such as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
(TILs), that have been reprogrammed to fight cancer. Other cell types, such as
skeletal muscle stem cells and neural stem cells, have shown promise in various
types of degenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and arthritis.
